December 11, 2014
Overview
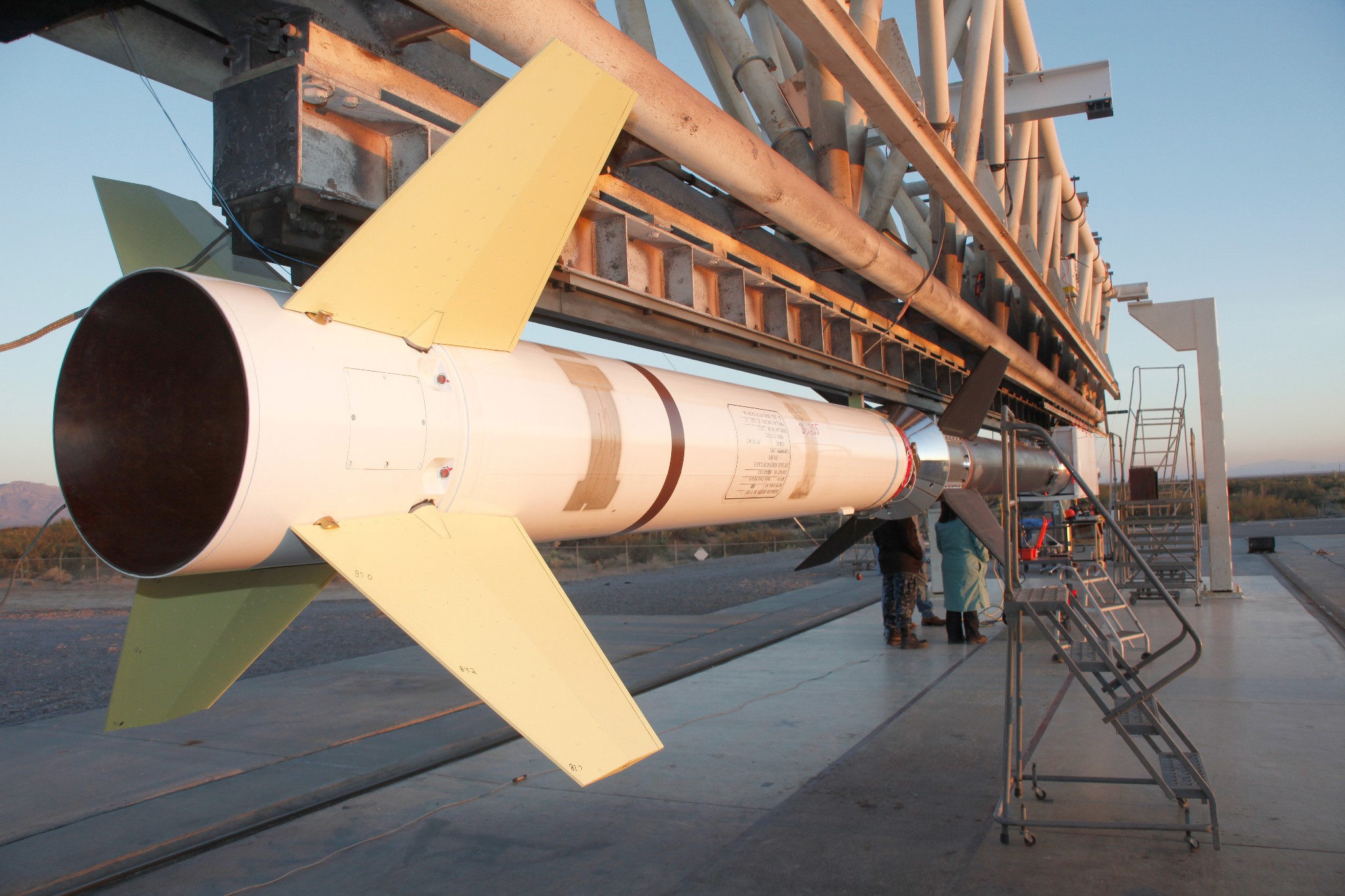
FOXSI-2 successfully launched on December 11, 2014 from the White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico. Our team made several key adjustments to the instrumentation from the first launch in an effort to better combat thermal blanketing and observe the quiet Sun. The flight lasted 6.5 minutes above 150 km, and our refurbished optics modules and detectors were able to capture fainter solar signals. To learn more about FOXSI-2 upgrades, read the full paper here.
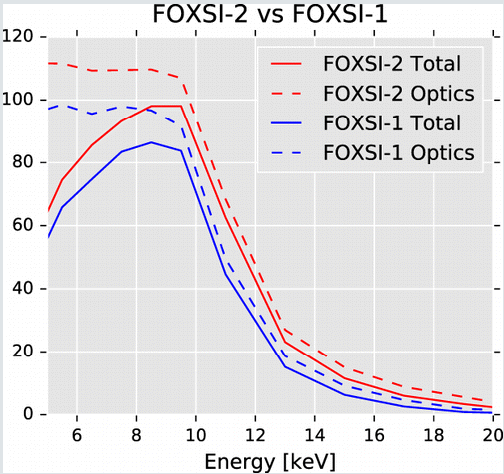
The graph depicts a comparison between the effective area provided by FOXSI-1 and FOXSI-2. For comparison, the optics area is also shown as dashed lines."
Instrumentation Characteristics
Optics
FOXSI-2 used five, seven-shell modules and two, ten-shell modules to increase the optics' effective area.
Detectors
Five of our optics modules used double-sided silicon (Si) strip detectors and the remaining two used double-sided cadmium telluride (CdTe) detectors for high efficiency at high energies compared to Si detectors.
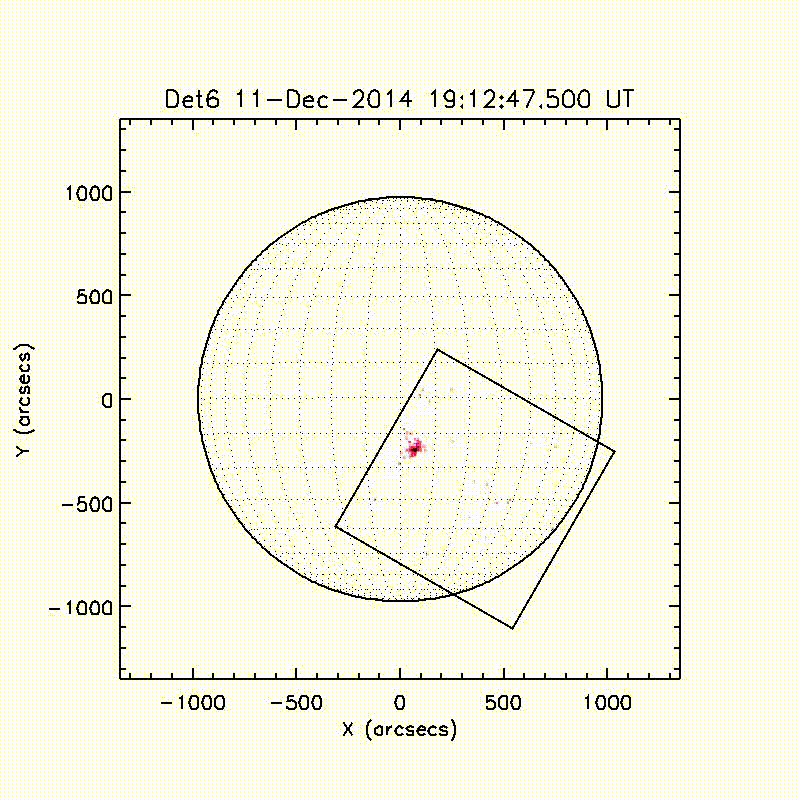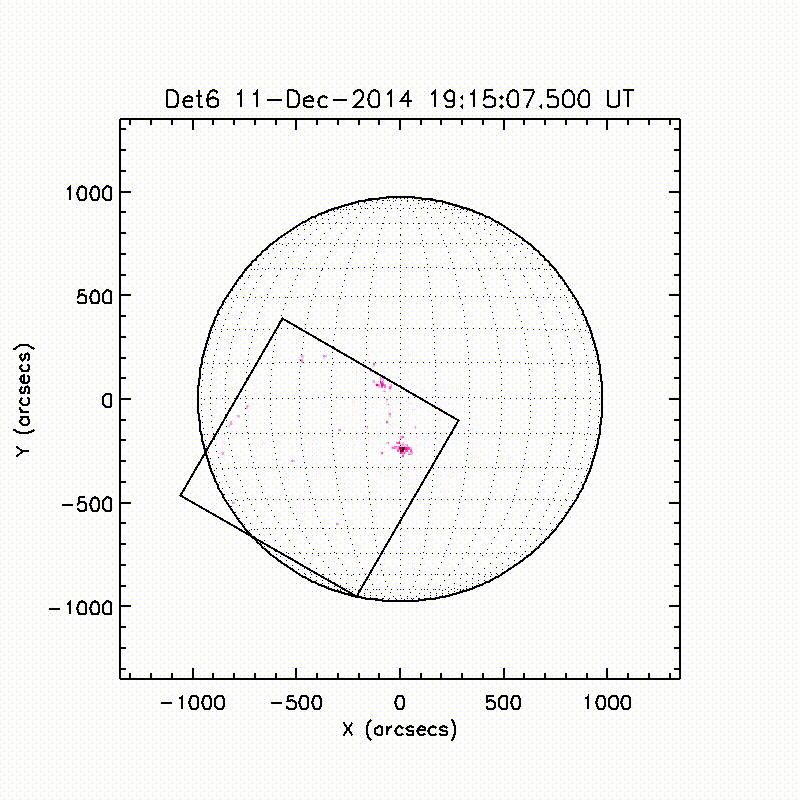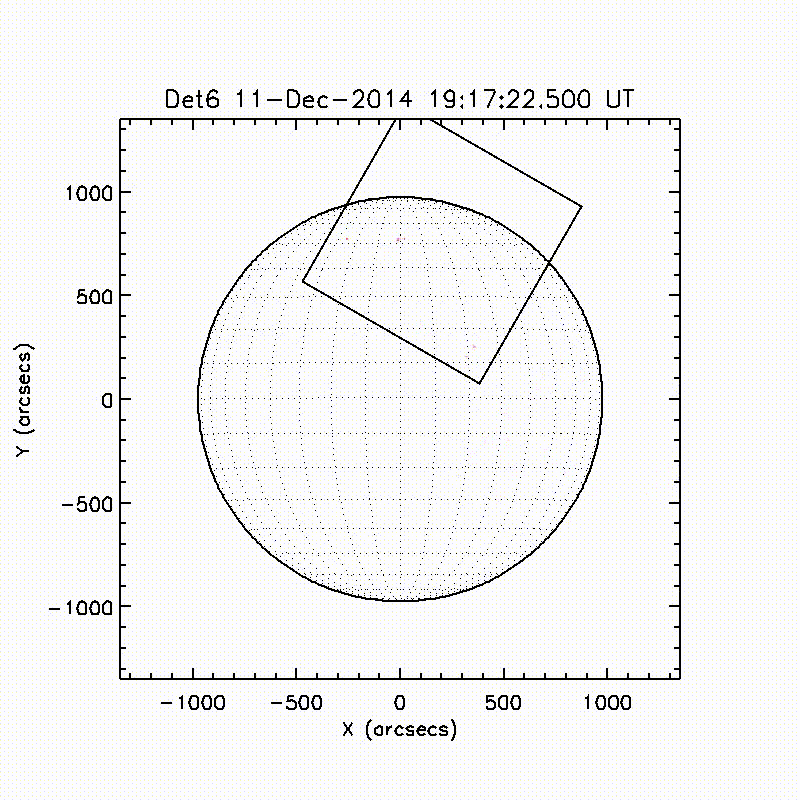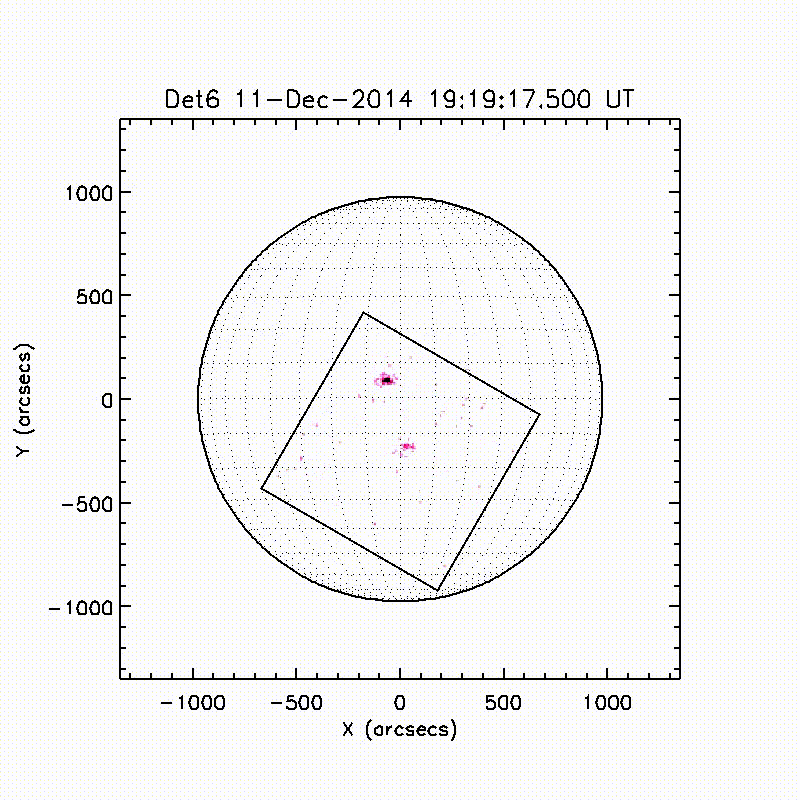
Launch & Observation Times
The FOXSI-2 launch was on December 11, 2014 at 19:11:00 UTC. Observation times were from 102 to 503.2 seconds after that time.
Coordinated Observations
- RHESSI (Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager)
- Hinode (EIS, XRT, SOT)
- IRIS (Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph)
- NuSTAR (Nuclear Sprectroscopic Telescope Array)
- VLA (Very Large Array)
Future Goals
- Discover more efficient ways to deal with high count rates
- Employ collimators to block “ghost rays” from non-targeted solar sources
- Test more detector options